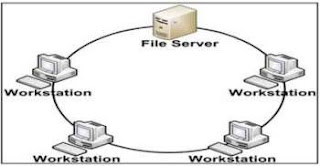
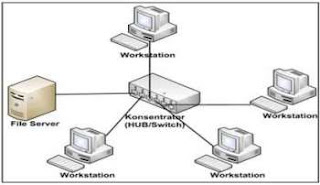
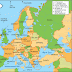
Secara astronomis Benua Eropa terletak antara 36°LU-71°LU dan 9°BB-66°BT. Luas daratan Eropa sekitar seperempat belas luas daratan di bumi dan menduduki peringkat ke-2 terkecil setelah daratan Australia. Benua Eropa membujur dari barat ke timur sejauh 5.300 km dan melintang 3.950 km. Luasnya adalah 10.900.000 km².
2. Batas Wilayah
Batas Kontinen sebelah timur ditetapkan di daratan mengikuti jalur puncak Peg. Ural dan Kaukasus terus ke Laut Kaspia.
Batas-batas benua Eropa adalah sebagai berikut.
a. Sebelah utara berbatasan dengan Kutub Utara (Arktik)
b. Sebelah selatan berbatasan dengan Benua Afrika dan Laut Tengah
c. Sebelah timur berbatasan dengan Selat Bosporus dan Laut HItam
d. Sebelah barat berbatasan dengan Samudera Atlantik
3. Bentang Alam
a. Perisai Baltik
Kawasan ini terdiri atas empat perisai batuan tua, diantaranya sebagai berikut.
1) Perisai Fenoskandia meliputu wilayah Norwegia, Swedia, dan Finlandia. Wilayah ini disebut negeri seribu danau
2) Pegunungan Skotlandia
3) Perbukitan Irandia barat laut
4) Pulau Eslandia
b. Dataran Raya Eropa
Kawasan ini meliputi Perancis, Belgia, Belanda, Jerman bagian utara, Denmark, dan sebagian besar Polandia. Pada permukaan daratan ini muncul pegunungan kecil dan pegunungan sisa (monadnock) yang kaya akan deposit batu bara.
c. Dataran Tinggi Tengah
Dataran Tinggi Tengah merupakan plato atau dataran tinggi yang terpotong-potong oleh dataran raya eropa. Tanahnya kurang baik untuk pertanian karena permukaan tanah yang tipis dengan kemiringan yang curam.
d. Pegunungan Lipatan Muda Alpin
Kawasan ini meliputi Pegunungan Alpin dan kelompok Pegunungan Mediteran. Pada Pegunungan Mediteran terdapat 3 semenanjung besar, yaitu semenanjung Pyrenia, Italia, dan Balkan. Puncak-puncaknya adalah Mount Blanck (4.807 m), Gunung Monte Rosa (4.634 m), Gunung Pico de Aneto (3.404 m), Gunung Mulchasen (3.478 m), dan Gunung Corno Grande (2.914 m). Pada Kawasan ini, pertanian kurang baik untuk diusahakan karena ketinggian tempat, lapisan tanah yang tipis, dan lereng yang curam.
e. Dataran Rusia
Permukaan dataran rusia ditutupi oleh lapisan tanah loss yang baik untuk tanaman gandum. Sungai-Sungai di dataran Eropa bermuara ke laut dan teluk, seperti Sungai Rhein dan Sungai Elbe ke Laut Utara, Sungai Wisla dan Sungai Oder ke Laut Baltik, Sungai Rhone ke Laut Tengah, dan Sungai Donau ke Laut Hitam.
Vegetasi Dataran Eropa dipengaruhi oleh keadaan tanah, keadaan air, iklim, dan topografi. Daerah paling utara ditutupi oleh tundra, sedangkan di bagian selatan ditumbuhi oleh semak berkayu keras (semak mediterania). Kawasan Eropa Timur dan tenggara merupakan daerah padang rumput. Pada kawasan beriklim laut dan peralihan ditumbuhi oleh hutan campuran dan hutan berdaun jarum.
4. Iklim
a. Iklim Laut
Tipe Iklim ini meliputi wilayah negara Eropa bagian barat laut, seperti Inggris, Skandinavia bagian barat, Perancis, Belgia, Belanda, Denmark, dan bagian utara Spanyol. Daerah ini memiliki musim dingin yang sejuk serta musim panas yang nyaman dan hangat dengan curah hujan yang cukup banyak.
b. Iklim Peralihan
Iklim tipe ini terdapat di Eropa Tengah dicirikan dengan musim dingin yang terasa lebih dingin dan musim panas yang masih hangat. Perbedaan suhu tahunan makin ke timur semakin tinggi karena semakin jauh dari pengaruh laut.
c. Iklim Kontinental (Daratan)
Iklim tipe ini terdapat di Eropa Timur bercirikan musim dingin yang lebih panjang dan berada di bawah titik beku. Hujan terjadi pada musim panas dalam jumlah kecil (kurang dari 25 inci).
d. Iklim Dingin dan Arktik (Kutub)
Daerah in dicirikan oleh musim dingin yang penjang dan temperatur berada di bawah titik beku. Musim panas yang pendek (3 bulan) dengan curah hujan kurang dari 5.000 mm. Kawasan iklim in meliputi Swedia bagian utara, Finlandia, Norwegia, dan Rusia.
e. Iklim Mediteran
Tipe iklim ini dicirikan oleh musim dingin yan basah dan musim panas yang kering, meliputi daerah Eropa bagian Selatan.
5. Keadaan Penduduk
Pada pertengahan tahun 2001 Benua Eropa berpenduduk 727.000.000 jiwa (sekitar 7%) dari jumlah penduduk dunia. Persebaran penduduknya tidak merata. Daerah yang padat penduduknya adalah Italia, wilayah pantai selatan, Jerman, Belanda, Belgia, Perancis, dan Inggris.
Dilihat dari pendapatan perkapitanya (PCI) yaitu sebesar US$ 10.025 Eropa termasuk kelompok negara maju. Rata-rata pendapatan per kapita dunianya adalah US$ 2.754. Angka harapan hidup mencapai 72 tahun dengan pertumbuhan penduduk sebesar 0,4%.
Berdasarkan ciri fisiknya, penduduk Benua Eropa dapat dibedakan atas beberapa kelompok.
a. Orang Nordik yang berambut pirang, seperti orang Norwegia, Swedia, dan Jerman.
b. Orang Alpen yang berambut lebih gelap dan tebal, diantaranya orang Perancis dan Swiss.
c. Orang Dinara yang berambut gelap, seperti oarang Rumania.
d. Orang Mediterania yang bertubuh pendek dan berkulit kekuning-kuningan, diantaranya orang Spanyol, Portugis, dan Italia.
e. Bangsa Slavia mencakup orang Rusia, Polandia, Ceko, Slovakia, Bulgaria, dan Yugoslvia.
Penduduk Benua Eropa memiliki lebih dari enam puluh bahasa dan ratusan dialek. Para ahli bahasa membedakannya dalam 3 rumpun bahasa.
a. Bahasa Indo Jerman dipergunakan oleh bangsa-bangsa di sekitar Laut Baltik, seperti orang Norwegia, eslandia, Swedia, Denmark, Inggris, Jerman, dan Belanda.
b. Bahasa Baltik Slavia meliputi bahasa Bulgaria, Ceko, Slovakia, Polandia, dan Rusia yang banyak digunakan di Eropa Timur.
c. Bahasa Romana meliputi bahasa Perancis, Italia, Spanyol, Portugis, dan Rumania yang digunakan penduduk di kawasan Eropa Barat.
Perkembangan bangsa-bangsa Eropa erat hubungannya dengan perkeembangan agama Kristen. Sekitar 50% umat Kristen yang menganut Katolik Roma tersebar di Eropa Barat, Tengah, dan selatan. Pemeluk agama Protestan tersebar di Skandinavia, Finlandia, Jerman, dan Belanda.
Umat beragama Ortodok Timur tersebar di bagian timur dan tenggara. apenganut agama lainnya 40 juta orang umat Islam, 4 juta orang umat Yahudi, dan umat agama lainnya.
2. Batas Wilayah
Batas Kontinen sebelah timur ditetapkan di daratan mengikuti jalur puncak Peg. Ural dan Kaukasus terus ke Laut Kaspia.
Batas-batas benua Eropa adalah sebagai berikut.
a. Sebelah utara berbatasan dengan Kutub Utara (Arktik)
b. Sebelah selatan berbatasan dengan Benua Afrika dan Laut Tengah
c. Sebelah timur berbatasan dengan Selat Bosporus dan Laut HItam
d. Sebelah barat berbatasan dengan Samudera Atlantik
3. Bentang Alam
a. Perisai Baltik
Kawasan ini terdiri atas empat perisai batuan tua, diantaranya sebagai berikut.
1) Perisai Fenoskandia meliputu wilayah Norwegia, Swedia, dan Finlandia. Wilayah ini disebut negeri seribu danau
2) Pegunungan Skotlandia
3) Perbukitan Irandia barat laut
4) Pulau Eslandia
b. Dataran Raya Eropa
Kawasan ini meliputi Perancis, Belgia, Belanda, Jerman bagian utara, Denmark, dan sebagian besar Polandia. Pada permukaan daratan ini muncul pegunungan kecil dan pegunungan sisa (monadnock) yang kaya akan deposit batu bara.
c. Dataran Tinggi Tengah
Dataran Tinggi Tengah merupakan plato atau dataran tinggi yang terpotong-potong oleh dataran raya eropa. Tanahnya kurang baik untuk pertanian karena permukaan tanah yang tipis dengan kemiringan yang curam.
d. Pegunungan Lipatan Muda Alpin
Kawasan ini meliputi Pegunungan Alpin dan kelompok Pegunungan Mediteran. Pada Pegunungan Mediteran terdapat 3 semenanjung besar, yaitu semenanjung Pyrenia, Italia, dan Balkan. Puncak-puncaknya adalah Mount Blanck (4.807 m), Gunung Monte Rosa (4.634 m), Gunung Pico de Aneto (3.404 m), Gunung Mulchasen (3.478 m), dan Gunung Corno Grande (2.914 m). Pada Kawasan ini, pertanian kurang baik untuk diusahakan karena ketinggian tempat, lapisan tanah yang tipis, dan lereng yang curam.
e. Dataran Rusia
Permukaan dataran rusia ditutupi oleh lapisan tanah loss yang baik untuk tanaman gandum. Sungai-Sungai di dataran Eropa bermuara ke laut dan teluk, seperti Sungai Rhein dan Sungai Elbe ke Laut Utara, Sungai Wisla dan Sungai Oder ke Laut Baltik, Sungai Rhone ke Laut Tengah, dan Sungai Donau ke Laut Hitam.
Vegetasi Dataran Eropa dipengaruhi oleh keadaan tanah, keadaan air, iklim, dan topografi. Daerah paling utara ditutupi oleh tundra, sedangkan di bagian selatan ditumbuhi oleh semak berkayu keras (semak mediterania). Kawasan Eropa Timur dan tenggara merupakan daerah padang rumput. Pada kawasan beriklim laut dan peralihan ditumbuhi oleh hutan campuran dan hutan berdaun jarum.
4. Iklim
a. Iklim Laut
Tipe Iklim ini meliputi wilayah negara Eropa bagian barat laut, seperti Inggris, Skandinavia bagian barat, Perancis, Belgia, Belanda, Denmark, dan bagian utara Spanyol. Daerah ini memiliki musim dingin yang sejuk serta musim panas yang nyaman dan hangat dengan curah hujan yang cukup banyak.
b. Iklim Peralihan
Iklim tipe ini terdapat di Eropa Tengah dicirikan dengan musim dingin yang terasa lebih dingin dan musim panas yang masih hangat. Perbedaan suhu tahunan makin ke timur semakin tinggi karena semakin jauh dari pengaruh laut.
c. Iklim Kontinental (Daratan)
Iklim tipe ini terdapat di Eropa Timur bercirikan musim dingin yang lebih panjang dan berada di bawah titik beku. Hujan terjadi pada musim panas dalam jumlah kecil (kurang dari 25 inci).
d. Iklim Dingin dan Arktik (Kutub)
Daerah in dicirikan oleh musim dingin yang penjang dan temperatur berada di bawah titik beku. Musim panas yang pendek (3 bulan) dengan curah hujan kurang dari 5.000 mm. Kawasan iklim in meliputi Swedia bagian utara, Finlandia, Norwegia, dan Rusia.
e. Iklim Mediteran
Tipe iklim ini dicirikan oleh musim dingin yan basah dan musim panas yang kering, meliputi daerah Eropa bagian Selatan.
5. Keadaan Penduduk
Pada pertengahan tahun 2001 Benua Eropa berpenduduk 727.000.000 jiwa (sekitar 7%) dari jumlah penduduk dunia. Persebaran penduduknya tidak merata. Daerah yang padat penduduknya adalah Italia, wilayah pantai selatan, Jerman, Belanda, Belgia, Perancis, dan Inggris.
Dilihat dari pendapatan perkapitanya (PCI) yaitu sebesar US$ 10.025 Eropa termasuk kelompok negara maju. Rata-rata pendapatan per kapita dunianya adalah US$ 2.754. Angka harapan hidup mencapai 72 tahun dengan pertumbuhan penduduk sebesar 0,4%.
Berdasarkan ciri fisiknya, penduduk Benua Eropa dapat dibedakan atas beberapa kelompok.
a. Orang Nordik yang berambut pirang, seperti orang Norwegia, Swedia, dan Jerman.
b. Orang Alpen yang berambut lebih gelap dan tebal, diantaranya orang Perancis dan Swiss.
c. Orang Dinara yang berambut gelap, seperti oarang Rumania.
d. Orang Mediterania yang bertubuh pendek dan berkulit kekuning-kuningan, diantaranya orang Spanyol, Portugis, dan Italia.
e. Bangsa Slavia mencakup orang Rusia, Polandia, Ceko, Slovakia, Bulgaria, dan Yugoslvia.
Penduduk Benua Eropa memiliki lebih dari enam puluh bahasa dan ratusan dialek. Para ahli bahasa membedakannya dalam 3 rumpun bahasa.
a. Bahasa Indo Jerman dipergunakan oleh bangsa-bangsa di sekitar Laut Baltik, seperti orang Norwegia, eslandia, Swedia, Denmark, Inggris, Jerman, dan Belanda.
b. Bahasa Baltik Slavia meliputi bahasa Bulgaria, Ceko, Slovakia, Polandia, dan Rusia yang banyak digunakan di Eropa Timur.
c. Bahasa Romana meliputi bahasa Perancis, Italia, Spanyol, Portugis, dan Rumania yang digunakan penduduk di kawasan Eropa Barat.
Perkembangan bangsa-bangsa Eropa erat hubungannya dengan perkeembangan agama Kristen. Sekitar 50% umat Kristen yang menganut Katolik Roma tersebar di Eropa Barat, Tengah, dan selatan. Pemeluk agama Protestan tersebar di Skandinavia, Finlandia, Jerman, dan Belanda.
Umat beragama Ortodok Timur tersebar di bagian timur dan tenggara. apenganut agama lainnya 40 juta orang umat Islam, 4 juta orang umat Yahudi, dan umat agama lainnya.